
Ethernet GPIB Controller for
PCs and Workstations
GPIB-ENET
 Features
Features
* Controls IEEE 488 instrumentation anywhere on an Ethernet-based TCP/IP network
* Up to 14 GPIB devices can be interfaced to each GPIB-ENET
* Shares GPIB equipment from several network hosts
* Compact size, 8.9 by 14.4 by 4.1 cm (3.5 by 5.7 by 1.6 in.)
* Built-in power supply - 100-120 or 220-240 VAC
* Two hardware versions available
- AUI and thin Ethernet (10Base2)
- AUI and twisted pair (10BaseT)
* IEEE 488.2 compatibility with the NAT4882 GPIB controller chip
* GPIB-ENET firmware code contained in Flash EPROM for easy upgrades and maintainability. No physical EPROM changes are required
* Driver software - NI-488.2M for HP-UX, NI-488.2M for OSF/1, NI-488.2M for Solaris, NI-488.2M for Windows 95, NI-488.2 for Windows, and NI-488.2 for Mac OS
* Application software - LabVIEW and LabWindows/CVI
Overview
Ethernet connectivity hardware is a standard feature of today's computers.
Most of these computers are connected
by a TCP/IP or similar network. Various operating systems for personal computers
also have built-in TCP/IP software capability. The GPIB-ENET Ethernet-to-GPIB
controller and corresponding NI-488.2 driver software take advantage
of this network connectivity in instrument control applications. Using the
GPIB-ENET, networked computers
can communicate with and control IEEE 488 devices from anywhere on an
Ethernet-based TCP/IP network. You can use a GPIB-ENET to share a single GPIB
system among many networked users, or to control several test systems from a
single networked host computer.
High-level NI-488.2M or NI-488.2 driver software is included with the GPIB-ENET
controller. The driver software programs the GPIB-ENET without the user having to
understand or program either Ethernet or IEEE 488 protocols. You can port
application programs written for other National Instruments GPIB interfaces for
use with the GPIB-ENET.
IEEE 488 and Network Interface Details - The GPIB-ENET converts a computer
with an Ethernet port using TCP/IP protocols into a GPIB Talker/Listener/
Controller (TLC). The GPIB-ENET implements the full range of GPIB Controller
functions and Ethernet-based TCP/IP protocols. It uses the National Instruments
Turbo488/NAT4882 GPIB Controller combination to handle the GPIB protocols. The
National Semiconductor ST-NIC
Ethernet controller handles the Ethernet protocols. The following paragraphs
describe the key components of the GPIB-ENET hardware.
Network Details - Because most work-stations are equipped with a network
interface, they also have one or more networking protocols. The TCP/IP protocols
are very common.
The Internet protocol gets its name from
the Internet, a global educational and scientific research network that uses the
Internet protocol to route information among network nodes. The Internet protocol
does not guarantee information delivery. The transmission control protocol
is used on top of the Internet protocol to guarantee correct, in-sequence data
between network hosts and devices.
Although the TCP/IP protocols are
commonly used on the Internet, most users of TCP/IP are not connected on
the actual Internet. Individual institutions and corporations have created their
own internal mini-Internet to interconnect their workstations and other network
hosts and devices that use TCP/IP.
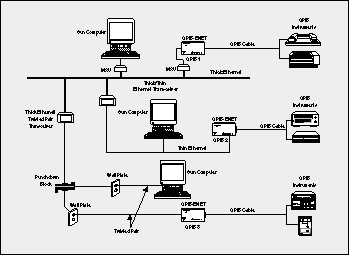 Figure 1 shows an example
of a local application of the GPIB-ENET. The versatile GPIB-ENET controllers can interface
to all three network cable types - thick Ethernet, thin Ethernet,
and twisted pair. In this example, three independent GPIB systems are connected
to the Ethernet using different cabling mechanisms. The regional application
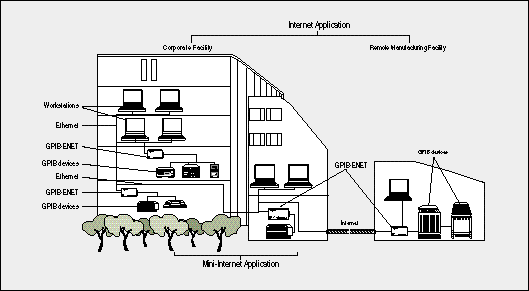
depicted in Figure 2 (page 4-64) shows
an example of a mini-Internet in a single building. The Internet application
example shows how a user on a workstation in a corporate facility can access a
GPIB-ENET installed at a facility in another location. Within the corporate
facility, a mini-Internet configuration connects workstations with other GPIB
devices, such as printers and plotters. Users can share GPIB systems throughout a
building, a complex, a country, or around the world. In the case of the Internet
example, the GPIB-ENET is used to extend the GPIB between the corporate office and
the manufacturing facility.
Figure 1 shows an example
of a local application of the GPIB-ENET. The versatile GPIB-ENET controllers can interface
to all three network cable types - thick Ethernet, thin Ethernet,
and twisted pair. In this example, three independent GPIB systems are connected
to the Ethernet using different cabling mechanisms. The regional application
depicted in Figure 2 (page 4-64) shows
an example of a mini-Internet in a single building. The Internet application
example shows how a user on a workstation in a corporate facility can access a
GPIB-ENET installed at a facility in another location. Within the corporate
facility, a mini-Internet configuration connects workstations with other GPIB
devices, such as printers and plotters. Users can share GPIB systems throughout a
building, a complex, a country, or around the world. In the case of the Internet
example, the GPIB-ENET is used to extend the GPIB between the corporate office and
the manufacturing facility.
Performance - To perform routing and
in-sequence, correct data transfers, TCP/IP protocols invoke significant software
overhead. In addition to the software overhead, each subnet displays unique
operating characteristics. Because of these reasons, data transfer benchmarking
is difficult with the GPIB-ENET. However, typical sustained throughput of data
can reach 50 kbytes/s.
Cabling - There are two cable configuration options for the
GPIB-ENET, the Ethernet AUI and coax (10Base2) version, and the Ethernet AUI and twisted-pair Ethernet (10BaseT)
version. A single configuration switch will select between the Ethernet AUI (attachment unit interface) and the other
option (coax or twisted-pair Ethernet). You can attach an Ethernet conversion
box to the GPIB-ENET AUI connector to convert between Ethernet media types.
Network Addressing - Each GPIB-ENET
is assigned a unique Ethernet address at the factory. This address is a 48-bit
value used to specify the source and destination of Ethernet packets.
The TCP/IP protocols also require an Internet address. This 32-bit value, which
has no relationship to the Ethernet address,
is used by the Internet protocol to locate devices on the network. There is an
Ethernet Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) facility that the GPIB-ENET
uses to be assigned an Internet address. The assigned Internet address is stored in non-volatile memory.
The Firmware - The necessary command interpretation, IEEE 488.2 and TCP/IP
protocol management, and system upkeep
of the GPIB-ENET are stored in Flash EPROM as an onboard firmware operating
system. Although code is installed at the factory, you can easily upgrade the
firmware by downloading new code to the GPIB-ENET memory. You can perform
the download procedure at your site with
a special utility provided on the distribution media. Firmware upgrades
are instantaneous; the physical EPROM inside the GPIB-ENET does not need to
be replaced.
Driver Software
The following NI-488.2M software is available for the GPIB-ENET:
* NI-488.2M for Windows 95
* NI-488.2M for HP-UX (HP Series 700)
* NI-488.2M for OSF/1 (DEC Alpha)
* NI-488.2M for Solaris 1 and 2 (Sun SPARCstation)
The following NI-488.2 software is available for the GPIB-ENET:
* NI-488.2 for Mac OS
* NI-488.2 for Windows
 Application Software
Application Software
You can use the following application software packages with the GPIB-ENET:
* LabVIEW
* LabWindows/CVI
GPIB-ENET Configuration Guide
Determine the following:
* How many GPIB-ENETs will be in the system
* What workstations will be controlling the GPIB-ENET(s)
* How many workstations of each type will be controlling the GPIB-ENET(s)
Case 1 - You have only one type of workstation (for instance, SunSPARCstation)
Case 2 - You have a mixture of workstations/computers that will control
GPIB-ENET systems.
1. Assign each group of similar workstations a GPIB-ENET
box. Allocate one GPIB-ENET hardware/software kit for each GPIB-ENET/workstation pair.
2. If there are GPIB-ENETs leftover, buy the corresponding number of GPIB-ENET hardware-only kits.
3. If there are any workstation groups leftover, buy the corresponding NI-488.2(M) software-only kit, which includes the multiple-user software license.
Part Numbers
Hardware and Software
HP Series 700
GPIB-ENET/HP-1 (single workstation) 776723-XY
GPIB-ENET/HP-2 (multiple workstation) 776724-XY
Sun SPARCstation
GPIB-ENET/Sun-1 (single workstation) 776631-0XY
GPIB-ENET/Sun-2 (multiple workstation) 776632-0XY
DEC Alpha
GPIB-ENET/OSF-1 (single workstation) 776917-XY
GPIB-ENET/OSF-2 (multiple workstation) 776918-XY
Windows 95 PC
GPIB-ENET/Win95-1 (single workstation) 777176-XY
GPIB-ENET/Win95-2 (multiple workstation) 777177-XY
Windows PC
GPIB-ENET/Win-1 (single workstation) 776921-XY
GPIB-ENET/Win-2 (multiple workstation) 776922-XY
Apple Macintosh
GPIB-ENET/Mac-1 (single computer) 776860-XY
GPIB-ENET/Mac-2 (multiple computer) 776861-XY
Hardware Only
GPIB-ENET 776933-XY
X = Ethernet connector type
1 = AUI /coax
2 = AUI /twisted pair
Y = Power cord type
1 = U.S. 120 VAC
2 = Swiss 220 VAC
3 = Australian 240 VAC
4 = Universal Euro 240 VAC
5 = North American 240 VAC
6 = United Kingdom 240 VAC
Software
NI-488.2M for
HP-UX (HP Series 700) 776725-01
Solaris (Sun SPARCstation) 776633-01
Windows 95 777179-01 OSF/1 776919-01
Windows 776923-01
Mac OS 776862-01
Includes a multiuser software license with which the user can install NI-488.2M software on multiple workstations within a single physical network.
| Computer/Bus | PC, Macintosh, HP Series 700, DEC Alpha, Sun SPARCstation, TCP/IP Ethernet |
| Processor | Intel x86, Pentium, Power PC, PA-RISC, Alpha, SPARC, Motorola 680x0 |
| Operating System | HP-UX, OSF/1, Solaris, Windows 95, Windows, Mac OS |
Specifications
Ethernet Port
National Semiconductor ST-NIC Ethernet controller chip
Ethernet address set by the factory or with a software utility
Internet address selectable by the Ethernet RARP facility and driver
configurable
IEEE 488 Compatibility
Full-function Talker, Listener, and Controller
Compatible with IEEE 488.1 and IEEE 488.2
Handles all primary and secondary addresses
Address is software selectable
Front Panel Indicators
Power - Power is applied to the GPIB-ENET
Ready - Self-tests have completed; ready for communications
Talk - GPIB-ENET addressed to source data on the GPIB
Listen - GPIB-ENET addressed to receive data from the GPIB
Transmit - Packets of data are transmitting onto the Ethernet
Receive - Packets of data are being received from the Ethernet
Link - Ethernet carrier signal is detected (10BaseT version only)
Performance
Maximum 50 kbytes/s sustained throughput
Physical
Dimensions 8.9 by 14.4 by 4.1 cm
(3.5 by 5.7 by 1.6 in.)
Weight 0.41 kg (0.9 lb.)
I/O Connectors
GPIB port IEEE 488 standard 24-pin
Ethernet port (option) AUI connection and either
thin Ethernet (10Base2) or
twisted-pair Ethernet (10BaseT)
Power Requirement (50-60 Hz)
100-120 VAC ± 10% 68 mA
220-240 VAC ± 10% 50 mA
Operating Environment
Temperature 0° to 40° C
Relative humidity 10% to 90%, noncondensing
Storage Environment
Temperature -20° to 70° C
Relative humidity 10% to 90%, noncondensing
Noise Emissions
FCC Class A verified
RELATED PRODUCTS
Hardware 4-42, 4-59
Software 2-10, 2-47, 2-106
Accessories 4-112 to 4-115, 4-119
